Description
Low-concentration solid particle aerosols produced from powders are required for many applications in research, development and quality assurance and for the calibration of particle measurement devices.
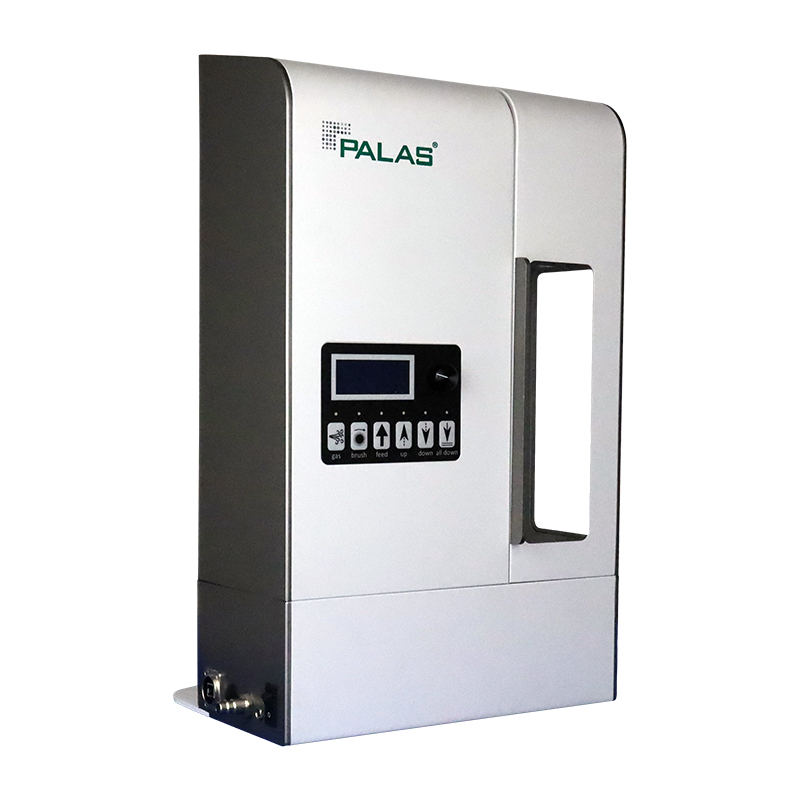
For more than 25 years, the RBG system has been used worldwide with great success for the reliable dispersion of non-cohesive powders such as mineral dusts, active pharmaceutical ingredients, pollen, etc. in the size range of < 100 µm and with a fine fraction of < 100 nm. Monolithic solid materials such as blackboard chalk are finely dispersed with highest dosing constancy.
The special advantage of this dosing and dispersion system is that in the case of the RBG system, mass flows ranging from approx. 40 mg/h up to approx. 800 g/h are dispersed with the highest level of dosing constancy thanks to quick, easy exchange of the solid material reservoir.
RBG basic can be operated with nitrogen as carrier gas.
Start-up
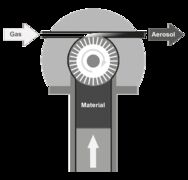
The powder to be dispersed is filled little by little into the cylindrical solid material reservoir and compressed with a tamper. The Lucerne University determined an excellent reproducibility of the tamping density in the solid material reservoir with a deviation of 3.4 %. The filled solid material reservoir is inserted into the dispersing head of the RBG. The powder, which has thus been uniformly compressed across the filling level, is then conveyed onto a rotating brush at a precisely controlled feed rate. An adjustable volume flow streams over the tightly woven precision brush at a very high speed and tears the particles out of the brush. The dispersing head assembly consists of a dispersing holder, dispersing cover, precision brush, and solid material reservoir.
Fig. 1: Schematic diagram of RBG system
Dosing
Dosing is performed via the precisely controlled feed rate of the feed piston. The desired mass flows can be easily and reproducibly specified based on the cross section of the solid material reservoir, the precisely adjustable feed rate of the feed piston and the easy-to-determine tamping density of the powder in the reservoir.
Mass flows of RBG system (compacted density 1 g/cm³)
|
Reservoir diameter
|
Fill quantity
|
Feed rate 1 mm/h
|
Feed rate10 mm/h
|
Feed rate 100 mm/h
|
Feed rate 1,000 mm/h
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
7 mm
|
2.7 g
|
38 mg/h
|
380 mg/h
|
3.8 g/h
|
38 g/h
|
|
10 mm
|
5.5 g
|
78 mg/h
|
780 mg/h
|
7.8 g/h
|
78 g/h
|
|
14 mm
|
17 g
|
150 mg/h
|
1.5 g/h
|
15 g/h
|
150 g/h
|
|
20 mm
|
35 g
|
310 mg/h
|
3.1 g/h
|
31 g/h
|
310 g/h
|
|
32 mm
|
88 g
|
800 mg/h
|
8 g/h
|
80 g/h
|
800 g/h
|
Dispersing
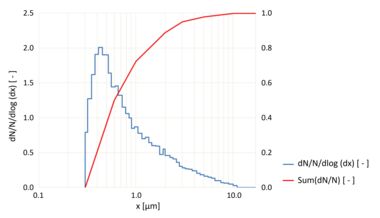
The powder separated from the reservoir by the precision brush is almost completely dispersed into the constituent particles (see Fig. 2), in the dispersing head by the dispersing air flowing at high speed. The dispersing air flow is regulated by manual setting of pre-pressure.
Fig. 2: Particle size distribution with the welas® digital 2000
Four different dispersing covers can be used for optimal dispersion.
Dispersion covers RBG system
|
Cover
|
Particle size
|
Reservoir diameter
|
Volume flow
|
Feed rate 100 mm/h
|
Feed rate 1,000 mm/h
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A
|
< 0.1 – 100 µm
|
7 – 32 mm
|
33 – 80 l/min
|
3,8 g/h
|
38 g/h
|
|
B
|
< 0.1 – 100 µm
|
7, 10 and 14 mm
|
17 – 40 l/min
|
7.8 g/h
|
78 g/h
|
|
C
|
< 0.1 – 100 µm
|
7 mm
|
8 – 20 l/min
|
15 g/h
|
150 g/h
|
|
D
|
200 – 1,000 µm
|
7 – 32 mm
|
33 – 80 l/min
|
31 g/h
|
310 g/h
|
|
32 mm
|
88 g
|
800 mg/h
|
8 g/h
|
80 g/h
|
800 g/h
|
Pulse mode
The construction design of the RBG system allows for operation in “powder”/”no powder” pulse mode with cycle lengths ranging down to a second. The function can be used manually on the unit or via a connected computer.
Remote control
RBG basic can be optionally controlled via the delivered software from a Windows computer or tablet.